big bluestem
Table of Contents

Andropogon gerardii Vitman
Alternate Common Names: turkey foot, turkeyfoot
Scientific Synonyms: Andropogon chrysocomus Nash, Andropogon furcatus Muhl. ex Willd., Andropogon provincialis Lam., Andropogon gerardii Vitman var. chrysocomus (Nash) Fernald
Family: grass family (Poaceae)
Functional Group: warm season grasses
Description
- Life cycle and growth form
Perennial with short rhizomes and fibrous roots that forms large clumps, a bunchgrass.
Height: 2-8 ft
- Leaves and stem
Leaves flat with a prominent midrib, 1-2 ft long and 1/4 in wide, often with long, unkempt, white hairs near leaf base and on lower sheath, ligule is a short, fringed membrane; flowering culms (stems) are erect and hairless, solid, often reddish to bluish purple in color with a waxy bloom, usually with a few branches near the top.
- Flower, fruit and seedhead
Fruit/seedhead: Seed heads (panicles) consist of 2-6 spikelike racemes 1.5-4 in long at the tips of branches, containing both seed-bearing and sterile flowers; seed heads appear bristly when mature and shatter from the tops especially on dry, windy days.
Pollination: wind
- Seed
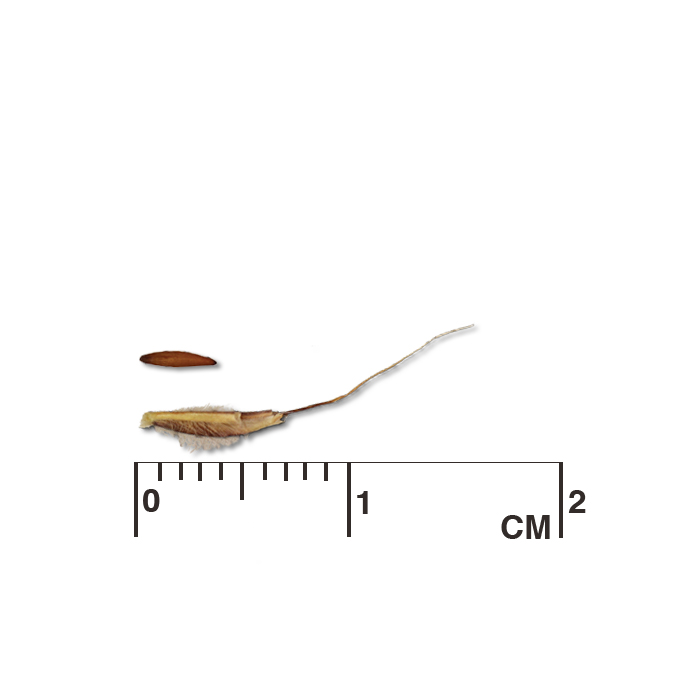
Seed characteristics
Seeds per ounce: 10,000 (IA NRCS)
Seeds per pound: 160,000 (IA NRCS)
1000 seed weight: 2.14 g (Seed Information Database)
Description: Fertile spikelet with awn, 1-2 cm long (1/2-3/4 in), attached stalk(s) are covered with hairs prior to debearding. Caryopsis smooth, brown, 3-5 mm long.
Typical seed test
PLS: 85%
Purity: 89%
Germination: 39%
Dormant: 56%
(averages obtained from 11 tests of purchased seed lots)
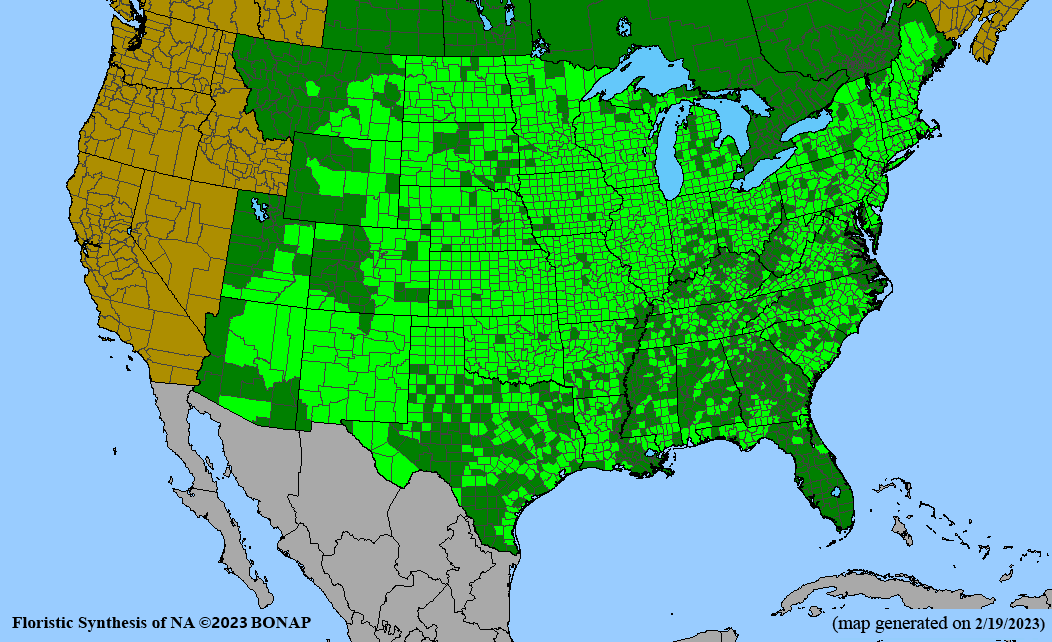
- Habitat and range
Habitat: Mesic to wet-mesic soil; full sun; prairies, savannas, roadsides, fens, glades. Wetland Indicator Status is Facultative (FAC) for the Midwest. Moist, loamy, deep, well-drained soils are preferred for seed production.
Conservation status: Global- G5, secure; Wyoming- S3, vulnerable (NatureServe)
General Comments
Big bluestem is a dominant component of the tallgrass prairie ecosystem. This species establishes readily from direct seeding, particularly if seeded into crop ground where good weed control has been achieved (i.e. following a glyphosate-resistant crop, for example). It takes two to three years for the stand to develop, with good management and weed control.
Recommendations for Seed Production
- Establishment for seed production
Direct seeding
Row spacing: 36 in 24 in 12 in solid stand PLS lbs/acre: 3.6 4.8 9.7 10-12 Seeding depth:1/4-1/2 in
Seeding method: native seed drill
Seeding time: mid to late spring
Weed control: Prepare clean, firm, weed free seedbed prior to seeding.
Greenhouse
Seed pre-treatment: No stratification necessary. Germination of grass seed usually improves with proper storage (cool, dry conditions) throughout the first year after harvest.
Sowing: Sow seed in greenhouse 2 months before last frost free date at 1/4 in depth.
Transplanting: Transplant after all danger of frost.
- Stand management
Weeds: During establishment - mow the stand 6-12 in high during first growing season to prevent weed canopy from shading seedlings. Established stand – Atrazine, 2,4-D, Plateau (imazapic), Outlook (Dimethenamid-P).
Pests: Yellow midges may infest florets, reducing seed yields.
Diseases: Smut fungus affects florets.
- Seed production
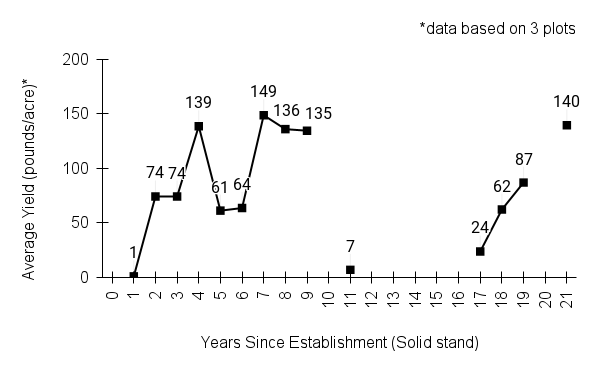
First harvest: Flowering and seed set end of second growing season from direct seeding, 3 years for stand to fill out.
Yield: 60-150 bulk pounds/acre (based on 3 solid stands with no supplemental nitrogen or irrigation; plots were not harvested every year)
Stand life: Peak harvests third year and after. If seed yields decline because stands are sod-bound, they can be chisel plowed to reinvigorate. Annual spring fire when green shoots are 2 in tall helps control weeds and increase flowering and seed production. (Note: This recommendation is strictly for production fields, not remnant prairies). Some producers use nitrogen application in spring to increase seed yield (60-100 pounds lb N/ac). Productive stand life 20 years or more.
Flowering date: early August - mid-September in northern Iowa
Seed maturity/Harvest date: October in northern Iowa
Seed retention: Shattering begins mid to late October.
Harvest date range at TPC (2003-2022): Sept 12 - Nov 2
Recommended harvest method: Combine at medium to hard dough stage, when some shattering is beginning to occur on the top of the main panicles.
- Seed cleaning and storage
Cleaning process: Air-dry material, scalp through 1/2 in mesh, remove awns with debearder or brush machine, then air-screen. Indent cylinder can help remove foxtail or similar weed seeds, if present.
Seed storage: cool/dry (33-50° F, 30-50% RH)
Released Germplasm
Source Identified material: Central (Zone 2), Northern (Zone 1), and Southern (Zone 3) Natural Selections/Iowa Ecotype Germplasm (IA), Northern Missouri Germplasm (MO), OH 370 Germplasm (OH), Southlow Michigan Germplasm (MI), Suther Germplasm (NC)
Selected germplasm: Bounty Germplasm (MN,SD), Hampton Germplasm (MO), OZ-70 Germplasm (AR, IL, MO, OK), Prairie View Indiana Germplasm (IN), Refuge Germplasm (AR, IL, MO, OK)
Cultivated variety (cultivar): Bison (ND), Bonilla (SD), Earl (TX), Kaw (KS), Niagara (NY), Rountree (IA), Sunnyview (SD)
- References
Chayka, K. (n.d.). Andropogon gerardii (big bluestem). Minnesota Wildflowers. https://www.minnesotawildflowers.info/grass-sedge-rush/big-bluestem
Hilty, J. (2019). Big bluestem - Andropogan gerardii. Illinois Wildflowers.https://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/grasses/plants/bigblue.htm
Houseal, G. A. (2007). Grasses warm season. In G. A. Houseal (Eds.), Tallgrass Prairie Center’s native seed production manual (pp. 66–67). Tallgrass Prairie Center - University of Northern Iowa.
Kartesz, J.T., The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2023. North American Plant Atlas. (http://bonap.net/napa). Chapel Hill, N.C. [maps generated from Kartesz, J.T. 2023. Floristic Synthesis of North America, Version 1.0. Biota of North America Program (BONAP). (in press)]
NatureServe. 2024. NatureServe Network Biodiversity Location Data accessed through NatureServe Explorer [web application]. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org/. (Accessed: February 29, 2024).
USDA-NRCS. (n.d.). Conservation plant releases. Natural Resources Conservation Service. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/plant-materials/cp/releases
USDA NRCS National Plant Data Team. (n.d.). Andropogon gerardii Vitman. USDA plants database. https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=ANGE
Species Guide Updated 12/17/2024