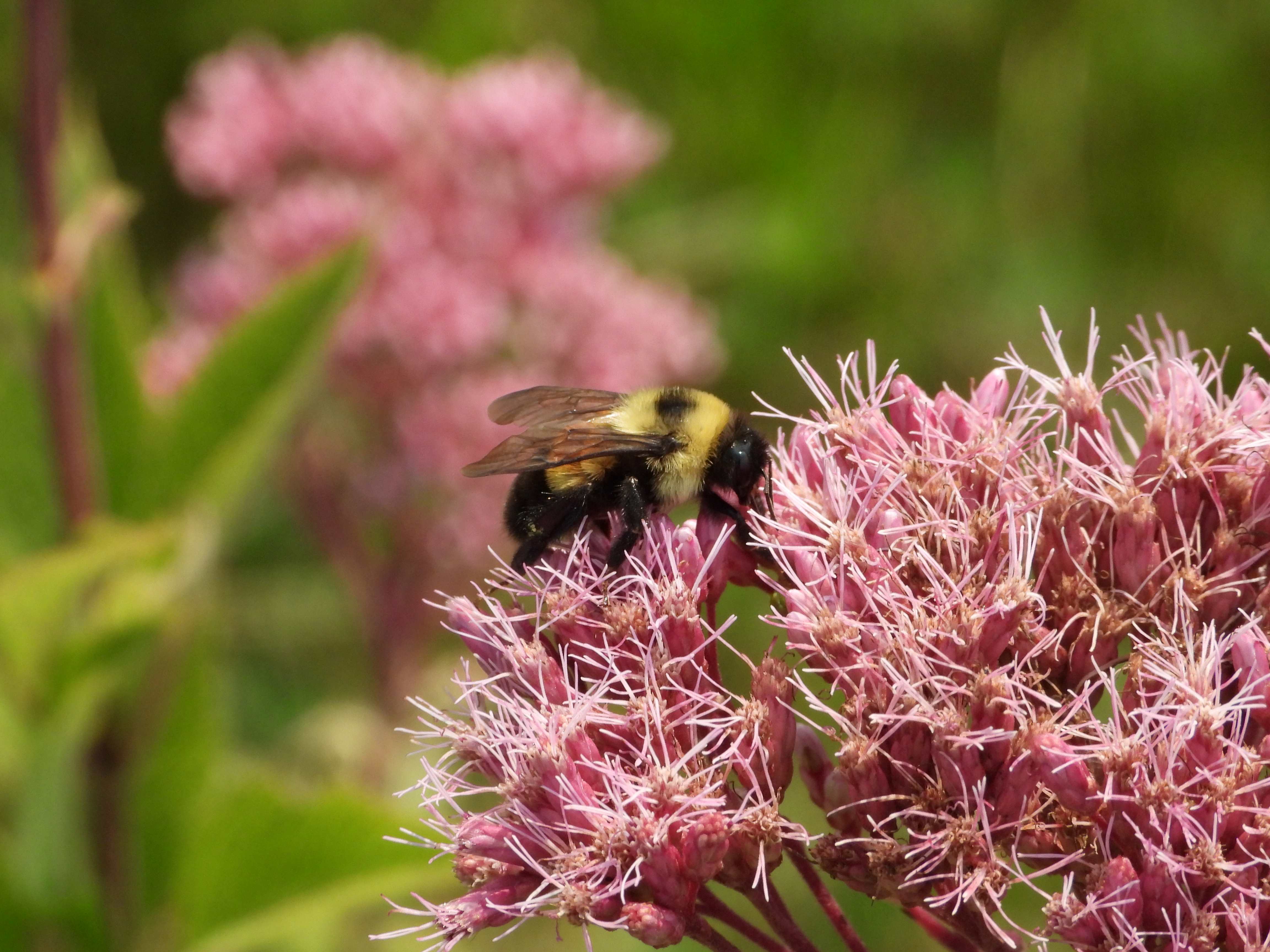
Eutrochium maculatum
spotted joe pye weed
Alternate names: purple boneset, spotted trumpetweed, Eupatoriadelphus maculatus, Eupatorium maculatum, Eupatorium purpureum var. maculatum
Family: Asteraceae, the aster, composite, or sunflower family
Functional group: forbs (wildflowers)
Description
- Life cycle and growth form
Perennial, spreads slowly by rhizomes to form clumps
Height: 2 - 10 ft (mostly 3 - 6 ft)

- Leaves and stem
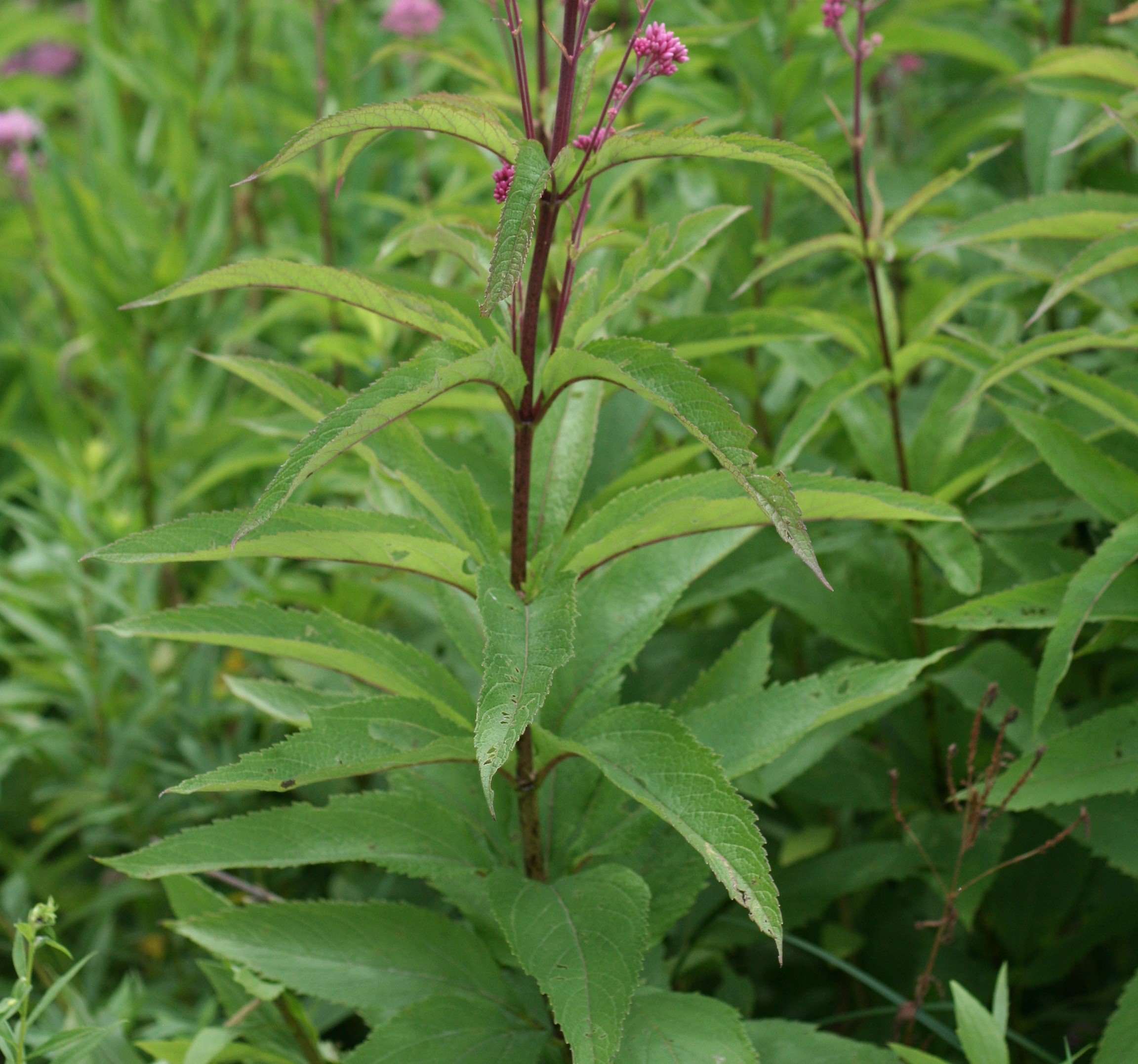

Lance-shaped, up to 9 in long with serrated margins, whorled in groups of 4-5 (usually) at each node, unbranched stems purple to purple-spotted (the name ‘maculatum’ means spotted and refers to this trait)
- Flower, fruit, seedhead
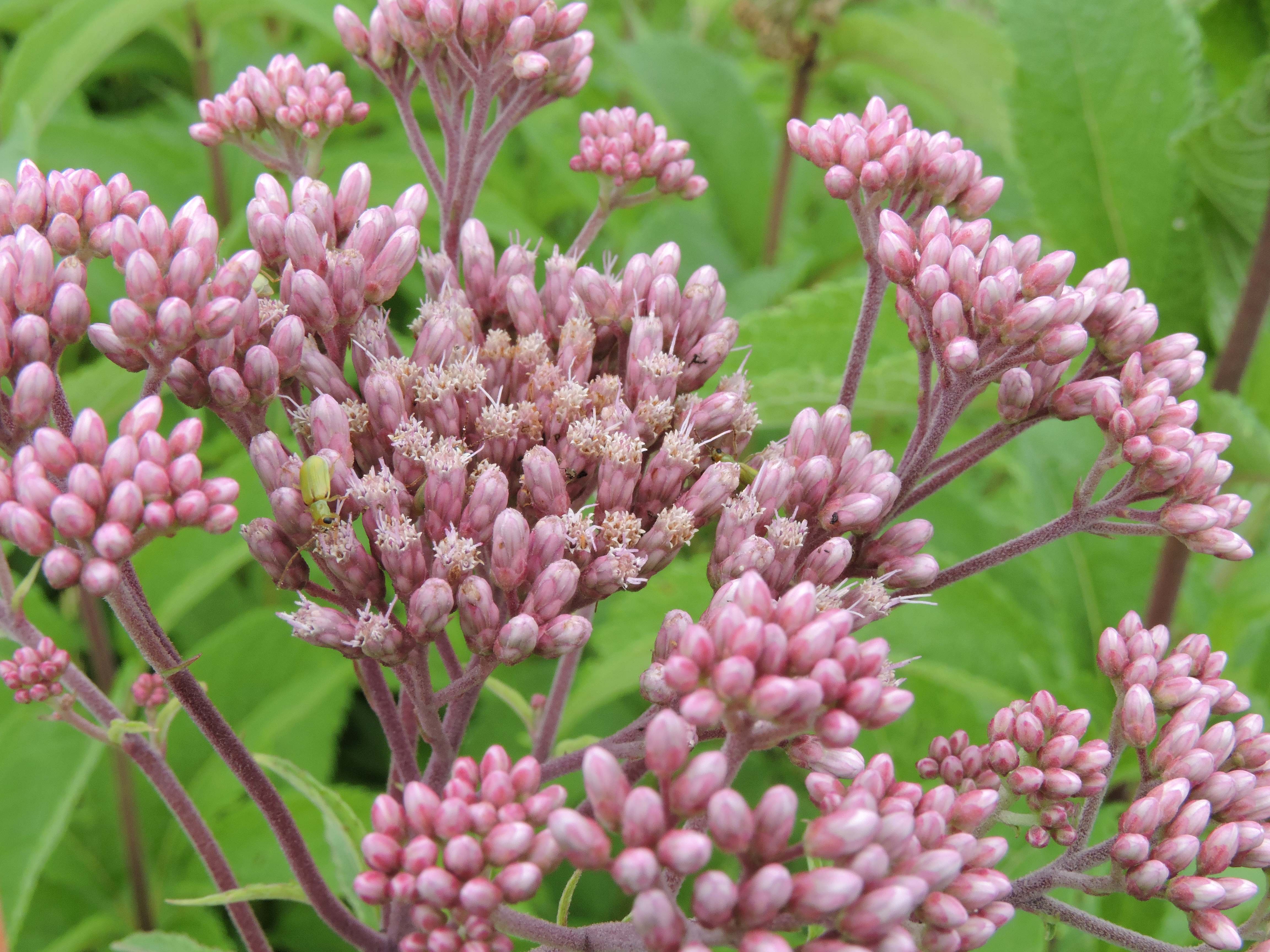
Flower: 3-5 small, indistinct florets per head, in flat-topped to domed inflorescences with dozens to hundreds of pink to purplish heads (rarely white); inflorescences appear fuzzy due to the long styles that stick out of the florets
Fruit/seedhead: seed clusters ripen from the center outward, becoming tan and fluffy as seed matures; seed is wind-dispersed and susceptible to shattering in windy weather

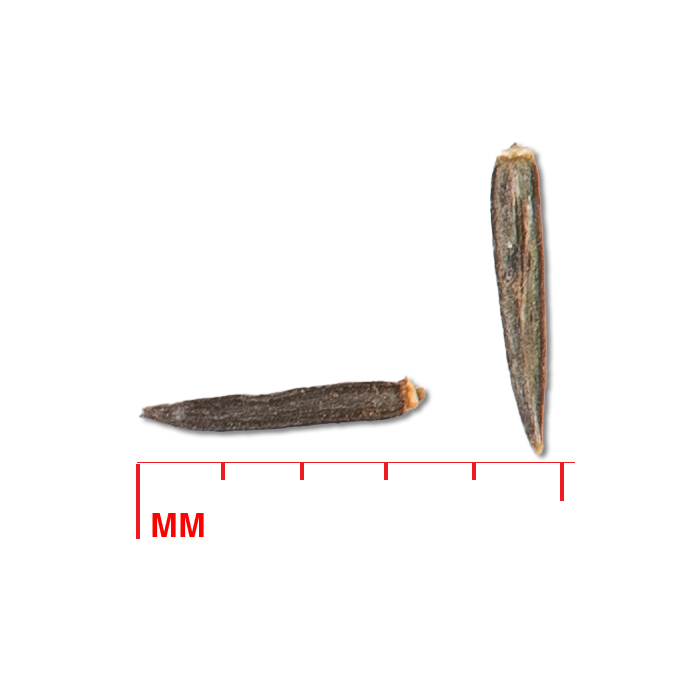
- Seed
Seed characteristics
Seed weight: 80,000 (Prairie Moon Nursery) 1000 seed weight: 0.28 g (Seed Information Database)
Description: slender, charcoal-gray seeds about 3 mm long with a tuft of tan pappus
Typical seed test:
PLS: 74%
Purity: 86%
Germination: 17%
Dormancy: 72%
- Habitat and range
Adaptation/habitat: spotted joe pye weed grows best in full sun and moist to wet soils. It is found in the wild in wet prairies, sedge meadows, fens, ditches, and other wet places. The USDA classifies it as an Obligate Wetland species in the Midwest region. It benefits from irrigation in production systems.
Threatened or endangered status: None listed in USDA Plants Database
Kartesz, J.T., The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2023. North American Plant Atlas. (http://bonap.net/napa). Chapel Hill, N.C. [maps generated from Kartesz, J.T. 2023. Floristic Synthesis of North America, Version 1.0. Biota of North America Program (BONAP). (in press)]
General comments
The sweet-scented flowerheads attract numerous and diverse pollinators including the endangered rusty patched bumble bee. We once identified seven species of butterflies along a 150 foot row of flowering spotted joe pye weed in one 15-minute observation. Traditional uses of this species by Native tribes include treatments for digestive, urinary, kidney, and women’s complaints and using the hollow stems as straws. The clumped stems and whorled leaves produce dense shade that excludes most weeds from a well-established plot. Irrigation is important for seed production.
Recommendations for seed production
- Establishment for seed production
Direct seeding (We do not have experience with direct seeding this species in seed production rows.)
Seeding rate:
Row spacing:
Seeding time:
Weed control:
Greenhouse
Seed pre-treatment: 60 days cold-moist stratification
Sowing: the seed is small and should be surface sown or very lightly covered or seedlings will not have enough energy to emerge. If started in germination flats, transplant to individual plugs when seedlings have their first pair of true leaves.
Transplanting: seedlings are ready to transplant to the field about 8-12 weeks after starting in plugs when their roots are well-branched and numerous root tips are visible at hole(s) in the base of the plug. Pop out a few plugs to check for adequate root development to provide sturdy plugs for planting. A week or two before transplanting, move flats outside to ‘harden off.’ (See the Propagation chapter in General Information for more details.)
- Stand management
Irrigate: necessary in most soils to obtain maximum seed yield.
Weeds: in the first season after transplanting, weeds are suppressed by a plastic weed barrier. Plants are spread by short rhizomes; in the second and subsequent years, holes in plastic must be expanded or plastic removed to make room for new stems. Well-established plots shade out most weeds.
Pests: no issues identified
Diseases: no issues identified.
- Seed production
First harvest: plants flower and set a little seed the first year when transplanted in spring
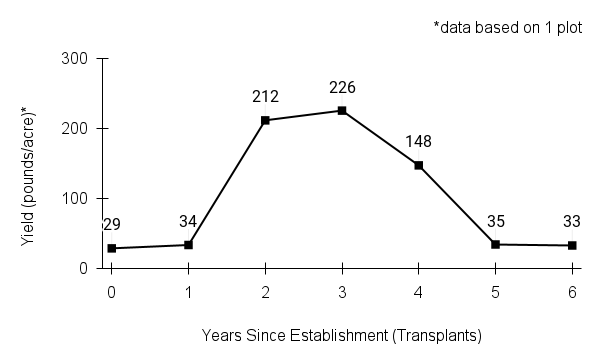
Yield per acre: 29-226 pounds/acre (see yield graph)
Stand life: peak seed production in years 3-5, but plants are long-lived and vigorous for many years
Flowering date: late July through early September (in NE Iowa)
Seed maturity: second to third week of September
Harvest date range at TPC (2016-2022): August 26 - October 3
Recommended harvest method: watch for the centers of seed clusters to begin shattering, and pick early maturing seed heads (clip stalks below seed clusters). If some heads in a cluster are still closed (not fluffy), pull apart a few heads to see if the seeds are dark-colored and separate easily from the base (receptacle). Combine the rest of the plot at peak maturity. Turn off the air or combine will disperse the fluffy seeds.
- Seed cleaning and storage
Cleaning process: if hand clipped, run dried material through a ¼” mesh to thresh seed from stalks. Use a brush machine (medium bristles, minimum vacuum) to remove pappus. Winnow with a box fan to separate the seed from most of the pappus and chaff. Airscreen 2-3 times to finish cleaning. See Appendix C for specific settings
Seed storage: orthodox (dry/cool)
Released Germplasm
Source identified material: Natural Selections/Iowa Ecotype Zone 1
Cultivated varieties: ‘Gateway’ is a compact cultivar used in landscaping
References
Eutrochium maculatum (Spotted Joe-pye Weed). Minnesota Wildflowers. (n.d.). https://www.minnesotawildflowers.info/flower/spotted-joe-pye-weed
Eutrochium maculatum. Prairie Moon Nursery. (2024). https://www.prairiemoon.com/eutrochium-maculatum-joe-pye-weed-prairie-moon-nursery.html
Missouri Botanical Garden. (n.d.). Eutrochium maculatum “Gateway.” Plant Finder. https://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?taxonid=302488&is
Native American ethnobotany database. (2003). http://naeb.brit.org/uses/search/?string=eupatorium%2Bmaculatum
SER, INSR, RBGK, Seed Information Database (SID). (2023). Eupatorium maculatum. https://ser-sid.org/species/567dc915-c79f-4608-a9d6-e1351ee9a2cb
Spotted Joe-Pye Weed. Illinois Wildflowers . (n.d.). https://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/wetland/plants/sp_joepye.htm
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. (n.d.). FWS-Listed U.S. Species by Taxonomic Group - All Plants. ECOS - Environmental Conservation Online System . https://ecos.fws.gov/ecp/report/species-listings-by-tax-group?statusCat…
USDA NRCS National Plant Data Team. (n.d.). Eutrochium maculatum (L.) E.E. Lamont. USDA plants database. https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=EUMA9
Species Guide Updated 2/13/2024




